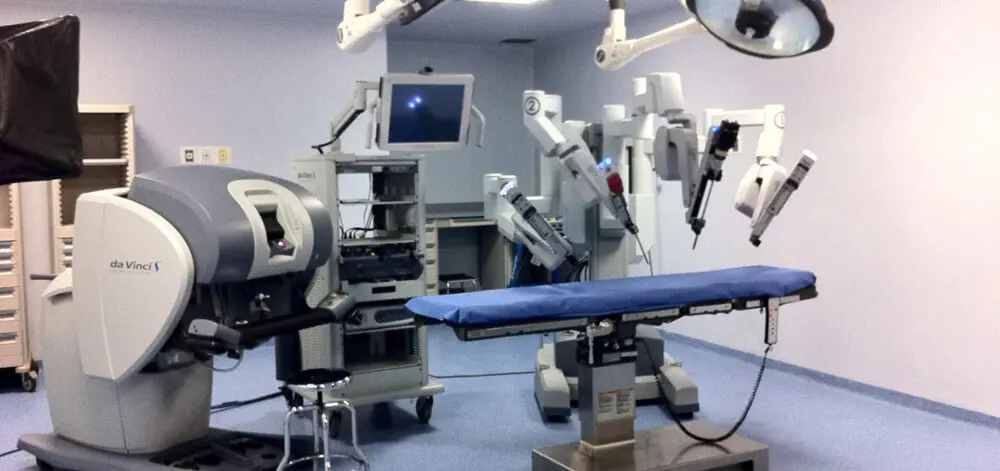
In a groundbreaking development, the Amrita Institute of Medical Science (Amrita Hospital) in India has achieved a significant milestone in the field of technology-assisted procedures. The hospital recently conducted a liver donor surgery utilizing the da Vinci surgical system, marking a remarkable advancement in the field of transplant surgery. This revolutionary approach not only ensures a safer alternative to conventional surgery but also promotes faster recovery and minimal scarring for donors. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of this breakthrough and explore how India has emerged as a hub for living donor liver transplants for foreign nationals.
The Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Traditional open surgery often leaves donors with a substantial scar on their upper abdomen, accompanied by prolonged pain and recovery periods. However, the da Vinci Surgical System introduces a new era of minimally invasive surgery, revolutionizing the way complex procedures like liver transplants are performed. Dr. S Sudhindran, the chief transplant surgeon at Amrita Hospital, highlights the key features of this innovative technology. The system's robotic arms, controlled by the operating surgeon, replicate the precise movements of a human hand, granting unparalleled accuracy and precision. Compared to conventional keyhole or laparoscopic surgery, the da Vinci system offers enhanced versatility, ensuring an optimal surgical outcome.
Get a free cost estimate
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery
The adoption of robotic surgery in liver transplants brings forth several advantages over traditional open surgery. Firstly, the minimally invasive nature of the procedure reduces the size of incisions, resulting in smaller scars and reduced post-operative pain for the donors. Additionally, the shorter recovery period allows individuals to resume their daily activities within a few months, enabling a faster return to a normal life. This advancement is indeed a boon for donors, alleviating their concerns about long-term discomfort and the need for an extended healing process.
India's Emergence as a Hub for Living Donor Liver Transplants
India has established itself as a global center for living donor liver transplants, attracting patients from various parts of the world seeking high-quality medical care at affordable costs. The availability of state-of-the-art facilities and a pool of skilled healthcare professionals have contributed to the country's prominence in the field. The introduction of robotic surgery techniques further solidifies India's position as a preferred destination for liver transplants.
India's expertise in living donor liver transplants is highly regarded, particularly for its success in performing surgeries for international patients. With a vast network of highly specialized hospitals and transplant centers, India offers a comprehensive ecosystem for medical tourism, providing personalized care and support to foreign nationals throughout their transplant journey. The inclusion of advanced technologies like the da Vinci Surgical System further bolsters India's reputation as a center of excellence for liver transplants.
Also Read:Breakthrough MitraClip Procedure in India
The successful implementation of robotic surgery in liver transplants at the Amrita Institute of Medical Science represents a significant breakthrough in the field of medical technology. The da Vinci Surgical System's precise and minimally invasive approach has revolutionized the way complex procedures are performed, ensuring improved outcomes and faster recovery for donors. India's emergence as a hub for living donor liver transplants, coupled with the adoption of advanced technologies, has further cemented the country's position as a global leader in medical innovation. With continuous advancements in surgical techniques, India is poised to contribute significantly to the field of transplant surgery and continue providing hope to patients in need of life-saving procedures.
Himang
Author
Himang Gupta is a skilled medical content writer with a Bachelor's degree in Biotechnology and extensive experience crafting engaging and informative blogs. Passionate about simplifying complex medical topics, he ensures his content resonates with readers. When not researching or writing, Himang enjoys scrolling Instagram, cracking jokes, and savoring the flavor of elaichi—his ultimate treat after a productive writing session.
Guneet Bindra
Reviewer
Guneet Bhatia is the Founder of HOSPIDIO and an accomplished content reviewer with extensive experience in medical content development, instructional design, and blogging. Passionate about creating impactful content, she excels in ensuring accuracy and clarity in every piece. Guneet enjoys engaging in meaningful conversations with people from diverse ethnic and cultural backgrounds, enriching her perspective. When she's not working, she cherishes quality time with her family, enjoys good music, and loves brainstorming innovative ideas with her team.